DPDK逻辑核与多线程
DPDK逻辑核与多线程
开始了漫长的看代码的道路. 从这篇文章开始, 少则一个函数, 多则一个example. 逐渐学习DPDK自带的一些例子程序. 希望通过这部分的学习, 能够很快实现数据包分析的线程绑定.
[TOC]
逻辑核结构体分析
这个是每个逻辑核的配置文件, 可以通过 core_id 来区分. 里面包含的是否可见, 状态, 以及运行的线程函数.
struct lcore_config { |
这个是整个运行环境的配置文件, 包含主线程核id, 逻辑核数量以及每个逻辑核的role, 进程优先级状态.
struct rte_config { |
/** |
环境抽象层初始化
环境抽象层 environment abstract layer[eal]
是对硬件资源的抽象, 即将硬件资源的细节内容隐藏起来, 只提供一些简单的接口来实现对资源的分配和利用.
eal 初始化函数
int rte_eal_init(argc, argv); // 实现代码 并未提供 |
是对环境抽象层的初始化, 只能在 Master_core 上运行, 并且越早执行它越好. 它使所有的逻辑核置于等待状态. 它在main 执行前结束初始化进程. 下面一句话来自代码注释, 并未懂, 等待以后考究:
* When the multi-partition feature is supported, depending on the |
这个初始化函数的返回值是 传递参数的个数 . 如果返回值ret大于等于0, 则初始化成功. 并且, 所有 argv[x], x< ret 的值都会被这个函数改变, 这些值不应该再被应用解释.
如果初始化失败, 会返回-1, 或者报错. 有以下几种错误:
* Error codes returned via rte_errno: |
逻辑核与线程相关API
线程启动任务
RTE_LCORE_FOREACH_SLAVE(lcore_id) {
rte_eal_remote_launch(lcore_hello, NULL, lcore_id);
}
其中RTE_LCORE_FOREACH_SLAVE(lcore_id) {} 是遍历所有逻辑核, 以lcore_id 为迭代器.
而最重要的一个api是:
int rte_eal_remote_launch ( lcore_function_t * f,
void * arg,
unsigned slave_id
)
函数参数:
lcore_function_t * f是要调用的线程函数.
void * arg是传递给这个线程函数的参数.
unsigned slave_id是执行这个线程函数的逻辑核的id. 同时也是这个线程的唯一标识~
返回值:
- 0: 如果成功的话.
- (-EBUSY): 如果目标核不是wait状态.
由此我们可以获得以下信息:
- 遍历所有逻辑核用 RTE_LCORE_FOREACH_SLAVE(lcore_id) { }
RTE_LCORE_FOREACH_SLAVE(lcore_id) { |
- 线程函数的指针类型是 lcore_function_t *
- 逻辑核id的类型是 unsigned. 他的大小是 4 Bytes
全部调用的一个直接api
int rte_eal_mp_remote_launch ( lcore_function_t * f, |
前面两个参数已经了解了, 第三个参数需要先了解一下 这个这个结构体:
enum rte_rmt_call_master_t |
意思就是, 看看主线程是否也需要这个任务! 跳过, 或者执行!
主线程等待
void rte_eal_mp_wait_lcore(void) |
他的作用是: 等待所有从线程执行完毕, 自己才结束, 相当于java中的 join 方法!!! 只能再主线程中使用!
int rte_eal_wait_lcore(unsigned slave_id) |
等待 slave_id 这个线程执行完毕, 如果该线程是running 状态, 则等待它执行到 finished状态. 如果这个线程已经是finished状态, 则将他置wait状态.
返回值: 如果是0, 那么这个线程已经是WAIT状态,
线程状态
下面是逻辑核的几种状态:
enum rte_lcore_state_t { |
enum rte_lcore_state_t rte_eal_get_lcore_state ( unsigned slave_id ) |
根据 slave_id 得到线程的状态.
线程中得到自己的信息
static unsigned rte_lcore_id (void ) //得到自己执行的应用线程的id |
static unsigned rte_get_master_lcore ( void ) //得到master core的id |
static unsigned rte_lcore_count ( void ) //得到系统上有多少个 逻辑核(执行单元) |
static int rte_lcore_index ( int lcore_id ) //得到核的index, 是从0 开始记数的 |
翻译出来可能不准确:
Return the index of the lcore starting from zero. When option -c or -l is given, the index corresponds to the order in the list. For example: -c 0x30, lcore 4 has index 0, and 5 has index 1. -l 22,18 lcore 22 has index 0, and 18 has index 1.
unsigned rte_socket_id ( void ) //得到这个核的 物理socket 的id |
static unsigned rte_lcore_to_socket_id ( unsigned lcore_id ) //根据 lcore_id 得到 |
static int rte_lcore_is_enabled ( unsigned lcore_id ) //返回的起始时 true 和 false |
static unsigned rte_get_next_lcore ( unsigned i, //当前的核id |
int rte_thread_set_affinity ( rte_cpuset_t * cpusetp ) //成功返回0 /否则 -1 |
void rte_thread_get_affinity ( rte_cpuset_t * cpusetp ) // 得到亲和度 |
int rte_thread_setname ( pthread_t id, |
int rte_lcore_has_role(unsigned int lcore_id,enum rte_lcore_role_t role ) |
这个需要先了解以下这个结构体:
/** |
所以这个api 的作用: 判断一个逻辑核 是否有 特定的角色, 是 返回0, 否则 为负数.
实战技能
看了这么多, 优点手痒想写个小程序.
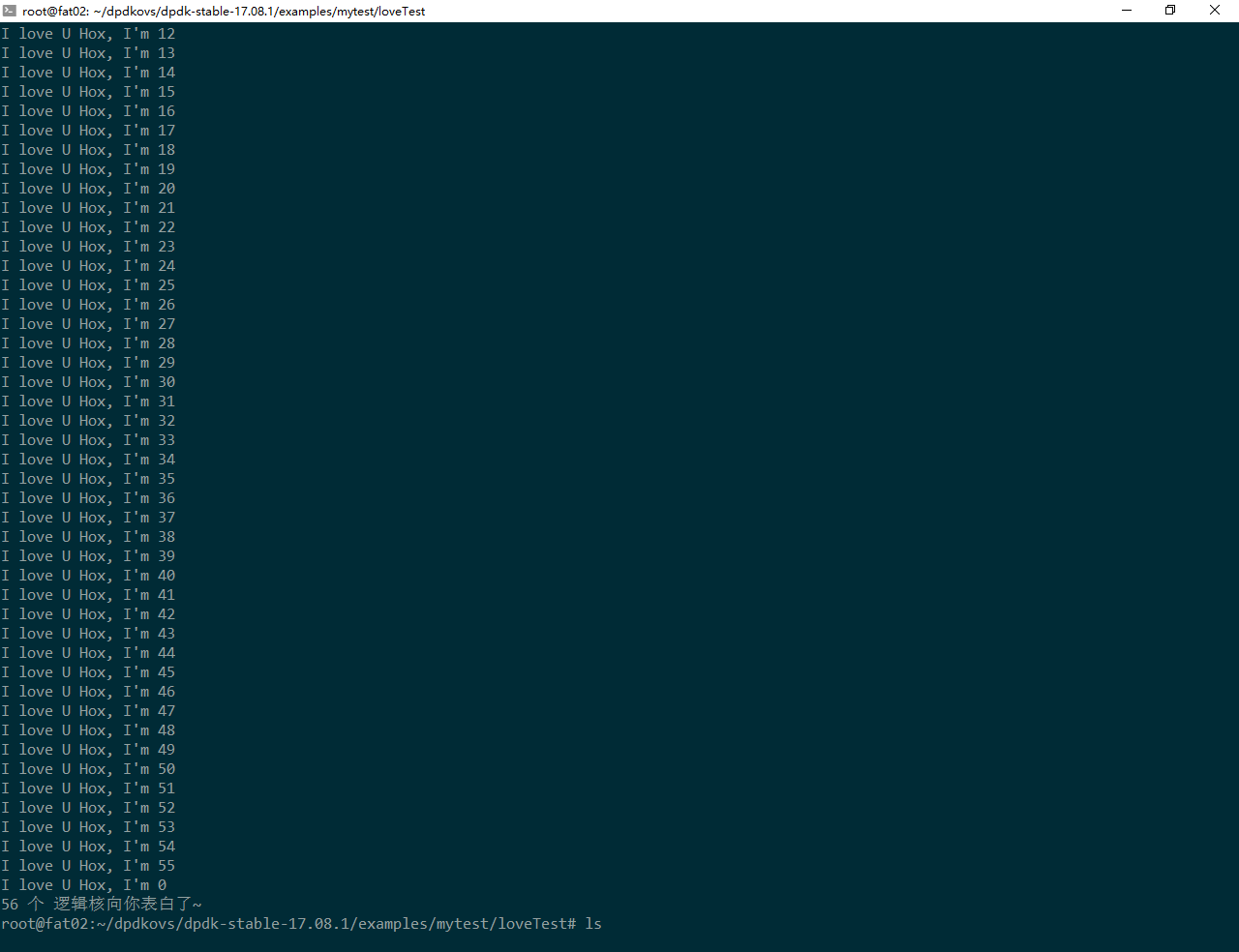
任务如下:
- 每个线程说一句: I love you Hox, I’m core x.
程序代码
|
效果截图